On the morning of March 11, 2024, the School of Computer Science and Technology at Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST) was invited to join and co-organized the "Computer-Assisted Medical Webinar" with the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology at Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM). The webinar featured splendid academic presentations by Professor Rahmita Wirza O.K. Rahmat, Associate Professor Iskandar Ishak from UPM, and Associate Professor Feng Lu from HUST. Dr. Ng Seng Beng from the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology at UPM chaired the webinar. Ybhg. Dato' Professor Dr. Shamala K. Subramaniam, Dean of the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology at UPM, attended the webinar and delivered a speech.
The webinar successfully opened under Dr. Ng Seng Beng's chairmanship. In his opening speech, Dr Ng Seng Beng emphasized the importance of applying computer science and technology in the medical and health field and expressed a positive outlook on the possibility of future interdisciplinary research.
Next, Prof. Dr. Rahmita Wirza O.K. Rahmat gave a fascinating presentation on "Research Directions in Computer-Aided Healthcare". She gave an in-depth overview of the innovative applications of computer technology in healthcare, including diagnostics, surgery, rehabilitation, and learning. Dr. Rahmat elaborated on the latest research findings in various subfields, such as Computer-Assisted Diagnosis (CAD), Computer-Assisted Surgery (CAS), and Computer-Assisted Radiation Therapy (CART).

She highlighted significant advances in computer-assisted medical in cardiovascular surgery, orthopaedic surgery, and neurosurgery to improve accuracy and efficacy through precise stent placement, bone cutting, implant positioning, and alignment in joint replacement surgeries. Professor Rahmat also shared her team's research work in medical image analysis, medical record-keeping, and medical simulation. She presented a series of related publications, intellectual properties, and research project grants.
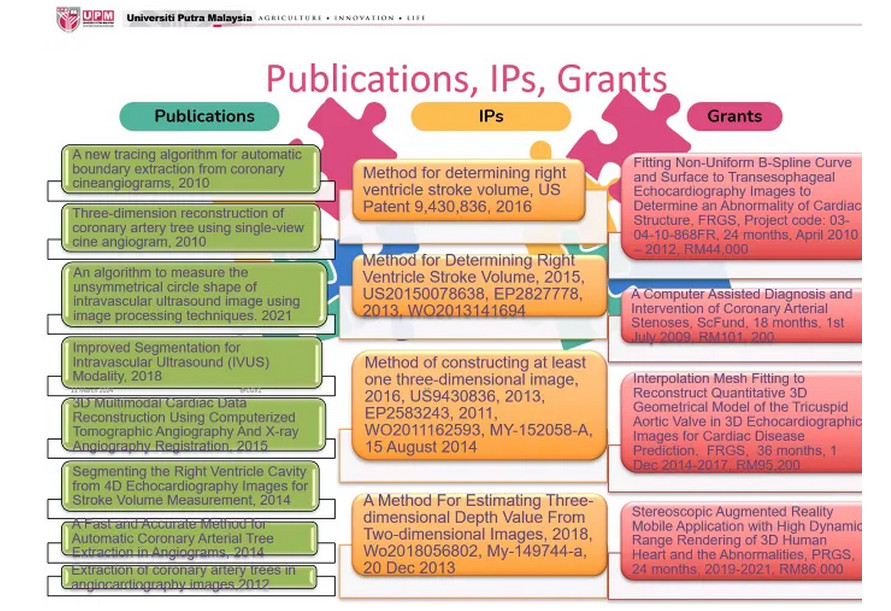
Furthermore, her presentation covered the latest computer-assisted cardiothoracic surgery technologies, including Computer Tomography Angiography (CTA), Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), and other advanced technologies that improve diagnostic and treatment processes. These technologies have played a crucial role in coronary artery CT angiography, transesophageal echocardiography, and digital subtraction angiography.

Professor Rahmat's presentation not only demonstrated how computer science has fueled the development of modern medical technology but also showed the great potential of interdisciplinary teams to improve the quality of patient care, increase productivity, and enhance healthcare outcomes through the close collaboration between medical imaging experts, healthcare practitioners, and computer-assisted medical experts. Her promising insights on the application of AI in the medical field, particularly her discussion of big data, datasets, diagnostic rules and image segmentation, provided attendees with an informative academic feast. Through her presentation, participants gained a glimpse of new trends in the future development of computer-aided healthcare, laying a solid foundation for further research and collaboration.
The second keynote speaker of the webinar, Associate Professor Ts. Dr. Iskandar Ishak, shared the research trends of the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology at UPM, highlighting the significant progress made in data science and machine learning.
Associate Professor Ishak began by introducing the history of the Faculty, which started offering diploma and bachelor's degree programs in the 1980s, established the Department of Computer Science in 1992, and eventually formed the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology in 1998. He mentioned that the Faculty comprises four departments: Department of Computer Science, Department of Software Engineering, Department of Communication and Network Technology and Department of Multimedia.

He detailed the faculty's research groups in data management, software engineering, network and distributed computing, and human-computer interaction. He highlighted the advanced work conducted by these teams in applying artificial intelligence in fields such as food safety, biodiversity, medical imaging and diagnosis, Industry 4.0, and education. In particular, he emphasized the significant contributions of the WiMoQ research group in wireless communication technology, mobile computing, and quantum computing.

When showcasing the Faculty's international collaboration network, he mentioned partnerships with several globally renowned companies and universities. These collaborations have diversified research and facilitated the formation of global research alliances. He also presented future research collaboration opportunities, including faculty and student exchanges, international research funding cooperation, joint supervision, and co-authored publications.

Through this online presentation, Associate Professor Ishak demonstrated the research capabilities of the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology at UPM and highlighted the faculty's active role in promoting disciplinary development and international cooperation.
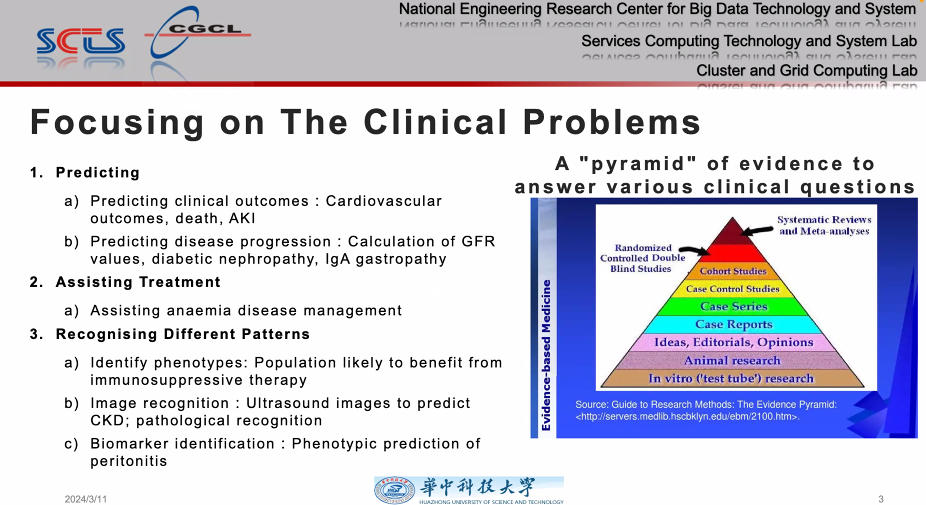
Associate Professor Feng Lu then gave an excellent presentation on "Early Warning and Risk Factor Analysis of Diseases Based on Artificial Intelligence". She introduced the steps of AI-based early warning and risk factor analysis, namely, focusing on clinical problems, meticulous data collection, AI model development, feature interpretation and extraction, and facilitating clinical applications.

First, she introduced the focus on clinical problems, including predicting clinical outcomes and disease progression, assisting treatment, and identifying and recognizing different phenotypes and biomarkers.
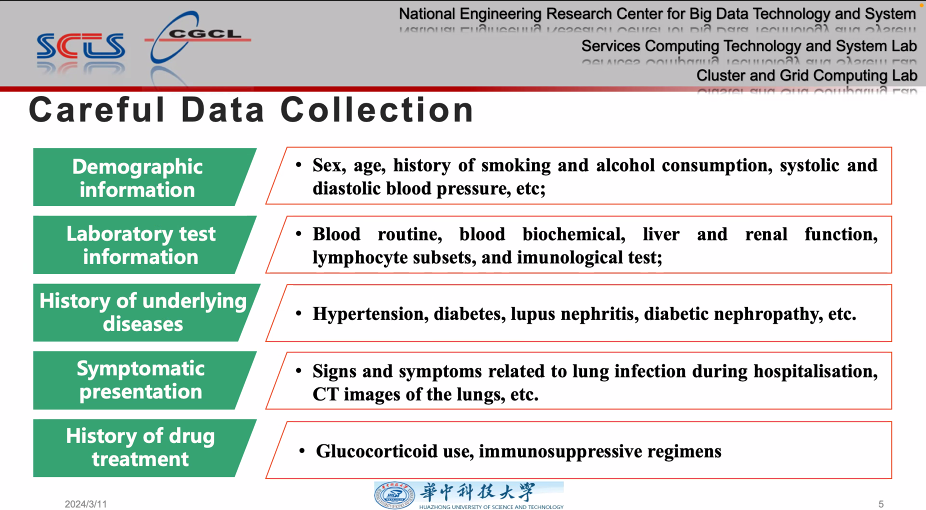
Furthermore, she demonstrated the process of data collection and processing in medical settings, emphasizing the importance of meticulous data collection for establishing accurate AI models. She explained in detail various data types, including demographic information, laboratory test results, medical history, and symptom manifestations. She also demonstrated how to perform semantic transformation and resampling on these data to eliminate model bias.
Regarding AI model development, Associate Professor Feng Lu used the example of subvisual observations of COVID-19 in CT images to illustrate how cross-image attention mechanism fusion methods can identify the hypervisual manifestations of COVID-19. She also showcased the early detection of femoral head necrosis, demonstrating how a transformer model based on symmetric sensitivity amplifies the abnormality of bilateral femoral head necrosis. This method enhances the model's predictive accuracy by utilizing specific convolutional blocks in the neural network to extract deep features from symmetric images of the femoral head and applying a symmetric difference loss constraint. These research achievements have not only been published in top conferences and journals but have also been cited on the official website of the World Health Organization (WHO), highlighting the international recognition of their research work and its potential practical application worldwide.

She also proposed an innovative method for sequence feature interpretation and extraction to improve the interpretability of model predictions. Finally, she shared her team's latest progress in facilitating clinical applications.

This presentation showcased Associate Professor Feng Lu and her team's profound expertise in medical clinical applications. It provided attendees with a vivid example of how to integrate medical knowledge with AI technology to drive advancements in the medical field.
During the online Q&A session, participants actively interacted with the scholars, discussing the critical issues of each presentation topic. They also delved into in-depth explorations of future research directions and challenges.
The success of this webinar showcased the latest research achievements in the fields of computer science and medicine. Besides, it strengthened the connection between interdisciplinary studies. The successful organization of the webinar enabled participants to communicate beyond geographical limitations and facilitated further collaboration between the two universities and research institutes. After the webinar, participants expressed their satisfaction with the limitless academic exchange platform provided by the webinar despite the constraints of face-to-face interactions. The School of Computer Science and Technology at HUST plans to expand the scope of online academic activities, deepen collaborations with global partners, promote interdisciplinary research, and jointly drive innovation and development in computer science and healthcare.
Universiti Putra Malaysia (UPM) is a public research university in Serdang, Selangor, Malaysia. Originally known as the University of Agriculture, UPM initially focused on agricultural science and related fields. However, since the 1990s, its disciplinary scope has expanded to include human ecology, linguistics, architecture, medicine, computer science, biotechnology, and other areas. UPM consists of 15 faculties, 11 research institutes, and 2 schools. Since 2006, UPM has been recognized as a research university and is one of Malaysia's five research universities. In 2023, it ranked 123rd in the QS World University Rankings and 25th among Asian universities, making it the third-best university in Malaysia.
